Twincharging: The Best of Both Worlds in Forced Induction
In the realm of automotive performance, the quest for more power never ceases. Engineers and enthusiasts alike are constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible under the hood. Among the myriad of innovations in engine technology, twincharging stands out as a fascinating fusion of two well-established forced induction methods. This cutting-edge approach combines the benefits of both supercharging and turbocharging, offering a solution that promises to deliver enhanced performance across the entire RPM range. But what exactly is twincharging, and why is it capturing the attention of performance car manufacturers and tuners worldwide?
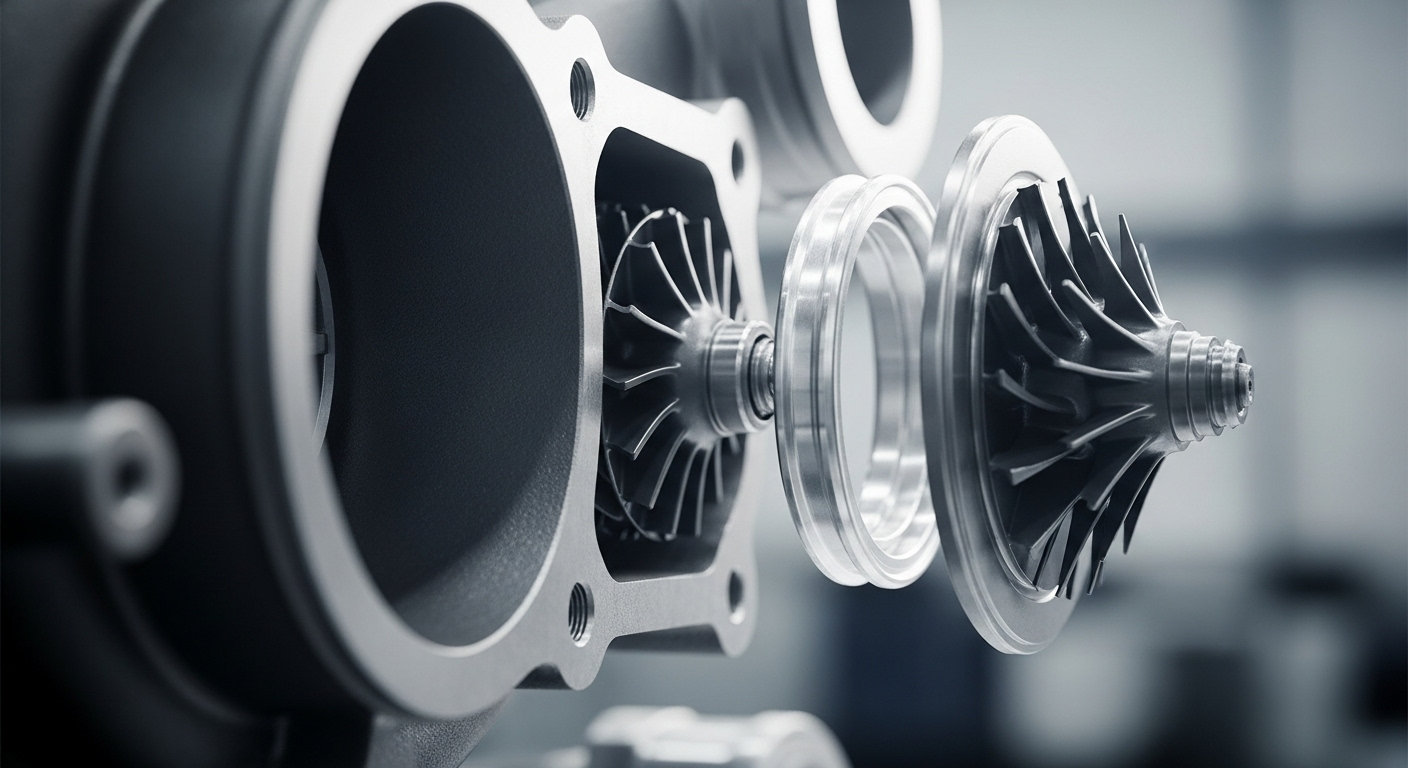
Superchargers: Instant Gratification
Superchargers are mechanically driven compressors that force air into the engine. Typically belt-driven by the engine’s crankshaft, superchargers provide an immediate boost in power as soon as the throttle is opened. This instantaneous response is their greatest strength, offering drivers a linear and predictable power delivery. However, superchargers consume engine power to operate, which can limit their overall efficiency, especially at higher RPMs.
Turbos: Efficiency at High RPMs
Turbochargers, on the other hand, are powered by the engine’s exhaust gases. As exhaust flows through the turbo, it spins a turbine connected to a compressor, which then forces air into the engine. Turbos are highly efficient at higher engine speeds, providing significant power boosts without directly sapping engine power. However, they suffer from lag at lower RPMs, as it takes time for exhaust pressure to build up and spin the turbine to effective speeds.
Twincharging: The Best of Both Worlds
Twincharging aims to combine the strengths of both systems while mitigating their weaknesses. In a twincharged setup, both a supercharger and a turbocharger work in tandem. The supercharger provides immediate boost at lower RPMs, eliminating turbo lag and ensuring responsive acceleration from a standstill. As engine speed increases, the turbocharger takes over, providing efficient power delivery at higher RPMs.
Implementation Challenges
While the concept sounds straightforward, implementing a twincharging system presents several engineering challenges. The complexity of managing two forced induction systems simultaneously requires sophisticated engine management systems. Engineers must carefully calibrate the transition between supercharger and turbocharger dominance to ensure smooth power delivery throughout the RPM range.
Thermal Management: A Critical Concern
One of the biggest hurdles in twincharging is managing heat. Both superchargers and turbochargers generate significant heat, and combining the two exacerbates this issue. Advanced intercooling systems are essential to keep intake air temperatures in check and prevent engine knock. Some twincharged setups even incorporate water-to-air intercoolers for more efficient heat dissipation.
Case Study: The Volkswagen 1.4 TSI Twincharger
One of the most notable implementations of twincharging technology came from Volkswagen with their 1.4 TSI engine. This compact powerplant combined a supercharger for low-end grunt with a turbocharger for high-end power, all in a small displacement package. The result was an engine that produced power comparable to larger naturally aspirated engines while maintaining better fuel efficiency.
The Future of Twincharging
As automotive manufacturers continue to face pressure to improve fuel efficiency without sacrificing performance, twincharging presents an intriguing solution. The technology allows for smaller displacement engines to produce power comparable to larger units, potentially offering a path to meeting stringent emissions regulations while still satisfying performance enthusiasts.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, twincharging faces several hurdles to widespread adoption. The increased complexity of these systems can lead to higher manufacturing costs and potential reliability concerns. Additionally, the added weight of two forced induction systems can impact vehicle dynamics and fuel efficiency gains.
A Niche Technology with Broad Implications
While twincharging may not become ubiquitous in the automotive world, its development and implementation showcase the ongoing innovation in engine technology. As manufacturers continue to explore ways to extract maximum performance and efficiency from internal combustion engines, twincharging stands as a testament to the ingenuity of automotive engineers. Whether it becomes a mainstream technology or remains a niche solution for high-performance applications, twincharging undoubtedly pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in automotive powertrains.




