Betta Fish Bubble Nests: A Marvel of Aquatic Architecture
Dive into the fascinating world of betta fish and their intricate bubble nests. These small but mighty aquarium inhabitants showcase remarkable engineering skills, creating elaborate structures that serve as both nurseries and courtship displays. Discover the science behind this captivating behavior and learn how it impacts betta fish care and breeding.
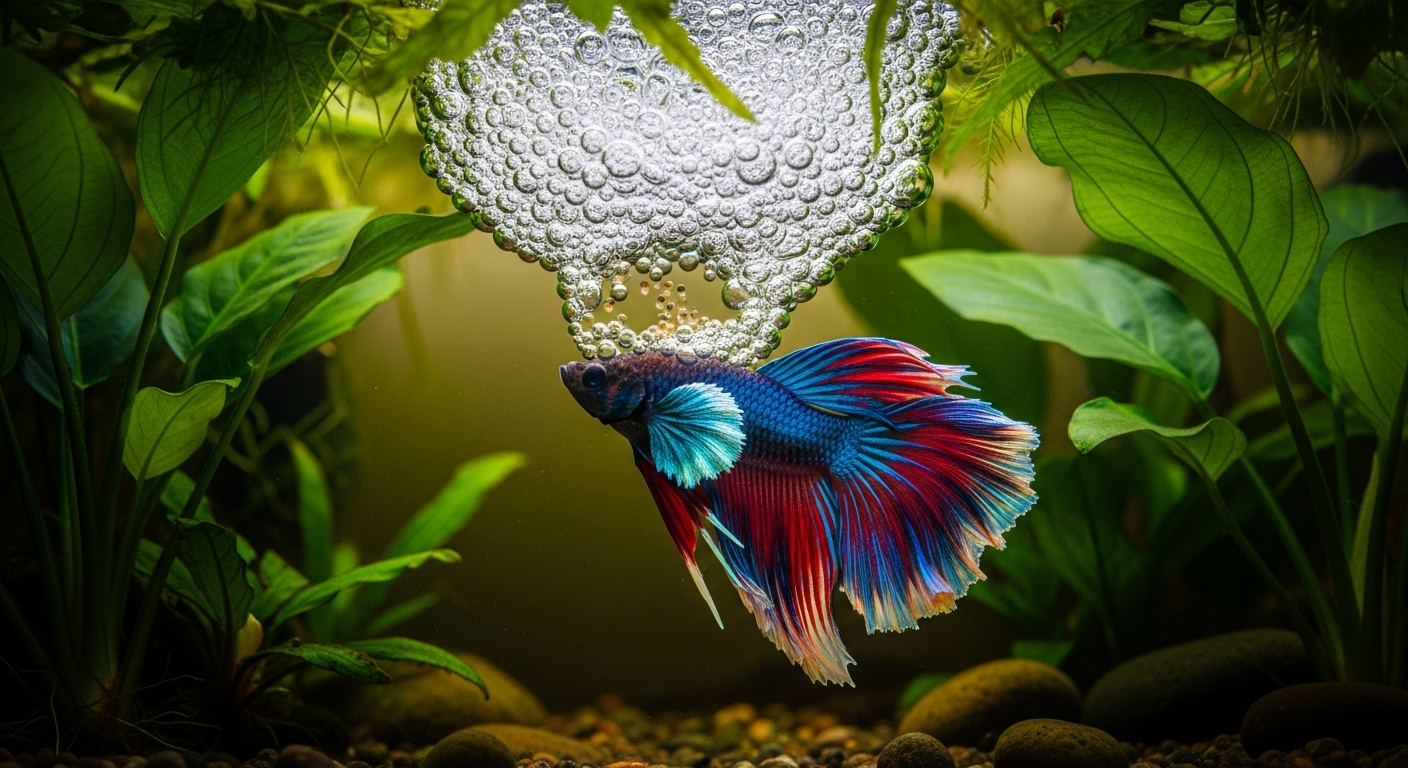

The Purpose Behind the Bubbles
Bubble nests serve multiple functions in the betta fish’s life cycle. Primarily, they act as a safe haven for eggs and newly hatched fry. The bubbles provide a protective environment, keeping the eggs oxygenated and free from harmful bacteria. Additionally, these nests play a crucial role in courtship rituals. A well-constructed nest signals to females that the male is healthy, capable, and ready to breed.
Environmental Factors Influencing Nest Building
Several factors can affect a betta’s inclination to build bubble nests. Water temperature, pH levels, and the presence of floating plants or debris all play a role. Typically, bettas prefer warm water between 78-82°F (25-28°C) for optimal nest-building conditions. Interestingly, even bettas kept in isolation may construct nests, driven by instinct rather than the immediate presence of a mate.
Bubble Nests in Captivity vs. Wild Habitats
While bubble nests are a common sight in home aquariums, their appearance and structure can differ in wild environments. In their natural habitats, such as the slow-moving waters of Southeast Asia, bettas often incorporate plant matter and debris into their nests. This adaptation provides additional stability and camouflage. In captivity, bettas may use floating plants or even small pieces of styrofoam as anchors for their bubble creations.
Implications for Betta Fish Care and Breeding
Understanding bubble nest behavior is crucial for betta enthusiasts and breeders alike. The presence of a bubble nest can be a positive sign of a healthy, content fish. However, it’s important to note that the absence of a nest doesn’t necessarily indicate poor health. For those interested in breeding bettas, providing optimal conditions for nest building is essential. This includes maintaining proper water parameters, offering suitable floating objects, and ensuring a stress-free environment.
The Science of Bubble Stability
The durability of betta bubble nests is a testament to the fish’s ingenuity. The bubbles are coated with a protein-rich mucus that increases surface tension, allowing them to withstand disturbances in the water. This coating also helps to keep the bubbles from merging, maintaining the nest’s structure. Research into this natural engineering feat has implications beyond the aquarium, potentially inspiring innovations in fields such as materials science and nanotechnology.
Evolutionary Significance of Bubble Nesting
From an evolutionary perspective, bubble nesting represents a successful adaptation to the betta’s native habitat. In shallow, oxygen-poor waters, this behavior ensures the survival of offspring by providing a well-oxygenated environment. The ability to construct these nests may have given bettas an edge over other species in their ecosystem, contributing to their widespread distribution across Southeast Asia.
Cultural and Historical Context
Bubble nesting behavior has long fascinated humans, playing a role in the cultural significance of betta fish in their native regions. In Thailand, where bettas are known as plakat, these fish have been bred for centuries, with bubble nest quality sometimes used as a criterion in selective breeding. This long-standing relationship between humans and bettas has contributed to the fish’s popularity in the global aquarium trade.
Future Research and Conservation Implications
As our understanding of betta fish behavior grows, so does the potential for conservation efforts. Studying bubble nesting in wild populations can provide insights into habitat health and the impacts of environmental changes. Additionally, research into the genetic factors influencing nest-building behavior may help in preserving the diversity of betta species and breeding lines.
In conclusion, the humble bubble nest represents far more than a quirky aquarium phenomenon. It’s a window into the complex world of betta fish behavior, offering lessons in biology, evolution, and even engineering. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of these aquatic architects, we gain not only a deeper appreciation for these remarkable fish but also potential insights that could benefit both science and conservation efforts.